
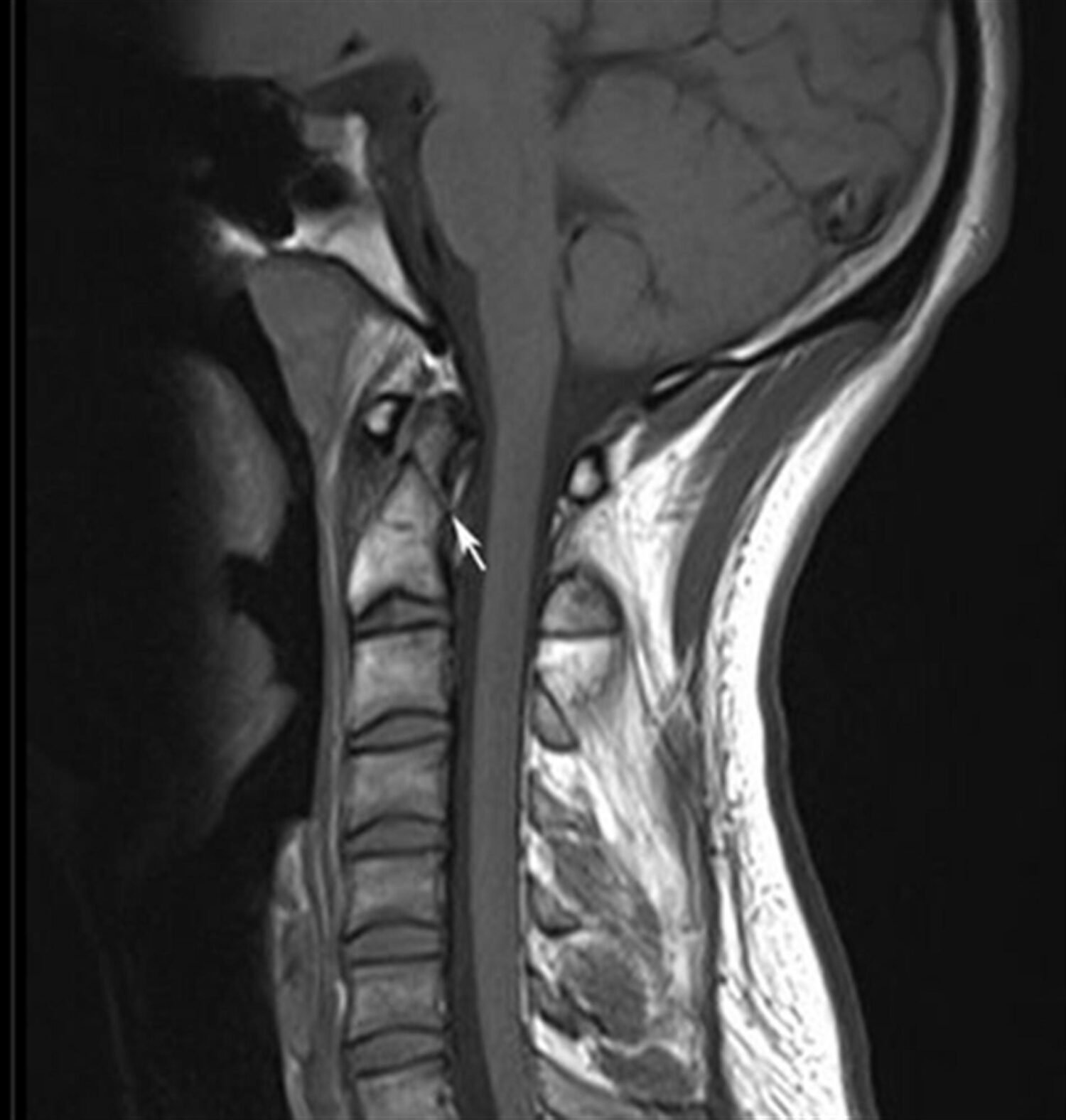
Īs they involve the body of the axis and have a relatively large surface area they are relatively stable and have a much lower risk of malunion ( Fig. Making it more unstable and definitely necessitating surgical stabilisation to prevent non-union ( Fig. Īlso involves additional chip fracture fragments at the base of the dens, Hadley et al suggested a modification of the Anderson & D’Alonzo classification system with the inclusion of a subtype of type 2 odontoid process fractures (type 2A). The risk of non-union is directly related to the degree of displacement ( Fig. Probably due to disruption of blood supply to the peg [5, With a risk of atlantoaxial subluxation if not promptly immobilised ( Fig. Or an associated occipital condyle fracture. They may be unstable if there is bilateral alar ligament avulsion, They are thought to be avulsion fractures of the alar or apical ligaments and occur above the level of the transverse ligaments, Type 1 odontoid process fractures are rare and somewhat controversial. Oblique fracture through upper part of the odontoid process caused by bony avulsion by alar ligamentsįracture at junction between the odontoid process and the body of the axisįracture that extends down into the cancellous bone of the body of the axis and is in reality a fracture of the body of C2 The fracture types may then be further classified as displaced or non-displaced. The classification system is summarised in Table 1 and Fig. They characterised odontoid peg fractures according the plane of the fracture. The Anderson and D’Alonzo classification system is the most widely used. Neurological injury is uncommon but due to the risk of atlantoaxial subluxation and proximity of the medulla oblongata, Odontoid fractures are the most common isolated cervical spine fracture in patients over the age of 70 years. Such as road traffic collisions in young or middle-aged patients.

Odontoid peg fractures are thought to occur following extreme hyperextension or hyperflexion of the cervical spine.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
